Hello Chemistry World
Welcome to the Epitome of Chemistry.
Your premiere blog for all things Chemistry related. Today we will be focusing on Acid-Base Neutralization. But firstly, we must define the terms acids, bases and neutralization.
An acid is a proton donor. Acids are substances that contain H+ ions when dissolved in water. Bases are proton acceptors. They contain OH- ions when dissolved in water. When an acid and a base react, they form salt and water. The type of reaction is a neutralization reaction.
Characteristics of Acids:
- taste sour when they are eaten
- can sting the skin when they are touched
- can corrode (or eat away at) metals and skin
- can be used as a reactant during electrolysis due to the presence of mobile ions
- turn blue litmus paper red
- are studied in chemistry and biology
- turn red or orange on universal indicator
Characteristics of Bases (Alkalis):
- Bitter taste (opposed to sour taste of acids)
- Slimy, or soapy feel on fingers
- Many bases react with acids and precipitate salts.
- Strong bases may react violently with acids. An acid spill can be safely neutralised by using a mild base.
- Bases turn red litmus paper blue
- Bases are substances that contain metal oxides or hydroxides
- Bases which are soluble in water form alkalis (soluble bases)
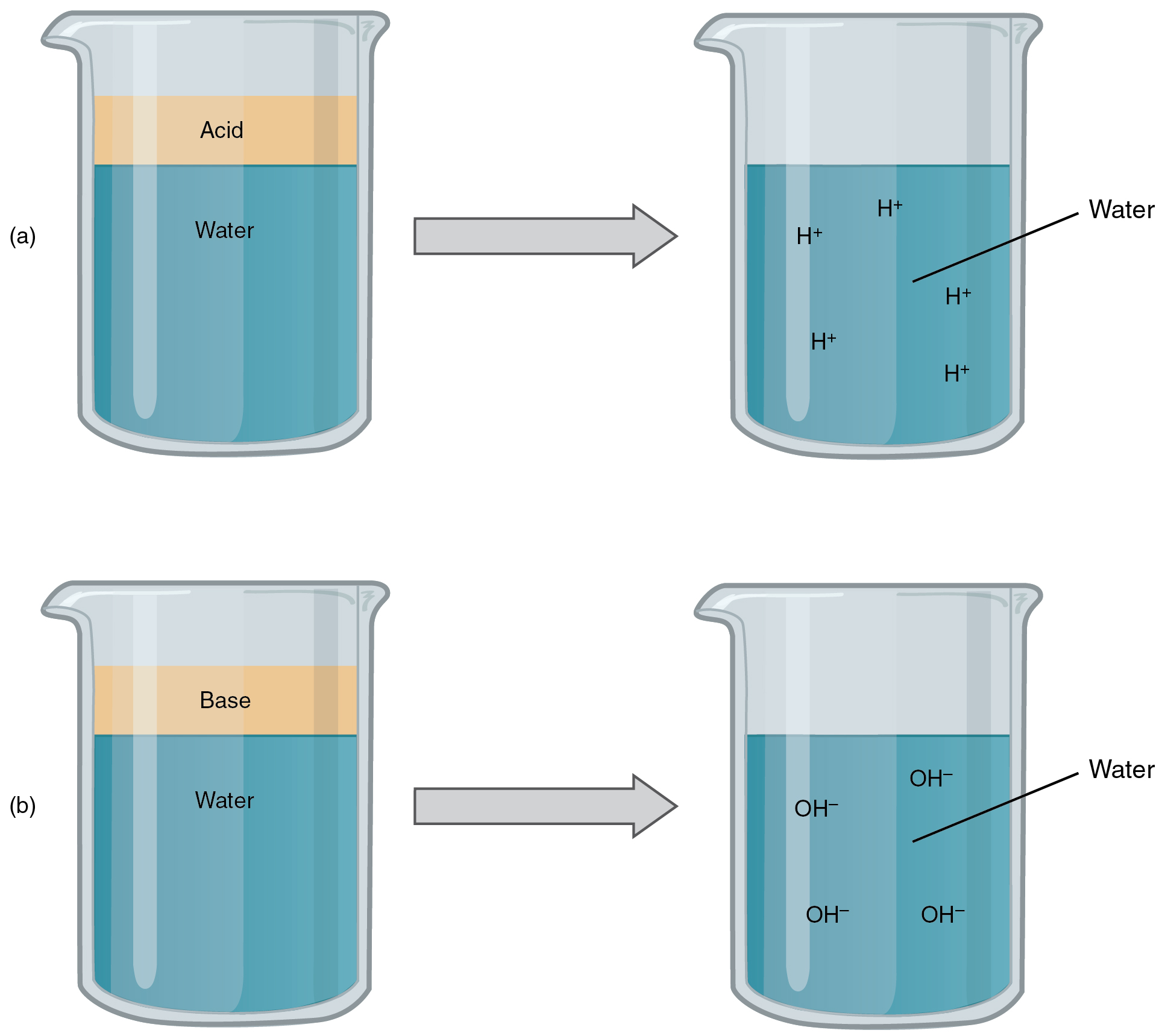
When acids and bases react, as we mentioned above that salt and water are formed. For example, when sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide sodium sulphate (salt) and water is formed. What you can see is that the sulphate ion in the acid bonds with the sodium ion in the base. The hydrogen from the sulphuric acid bonds with the hydronium ion from the base.
Now, it is your time to name the salt formed when acids and bases react. Please explain what happens and the products formed.
1. Hydrochloric acid and potassium hydroxide reacts
2. Sulphuric acid and calcium oxide
3. Sulphuric acid and calcium hydroxide
4. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide
Real-life Application of neutralization
Acid and base neutralization is a part of our everyday life. Here are some examples of acid-base neutralization in our everyday lives.
1. Stomach burn caused by acids is neutralized by antiacids
2. Bee stink is acidic, so it is neutralized with baking soda
3. Wasp stink is basic, so we neutralize it with vinegar
Here is a video providing you with more real-life applications
My challenge for you is to evaluate the benefits of neutralization reactions in your life. State what would happen if there was no neutralization reaction in your life.
Comments
Post a Comment